BYPASS Samples and Spectra
Data currently ingested in the BYPASS database
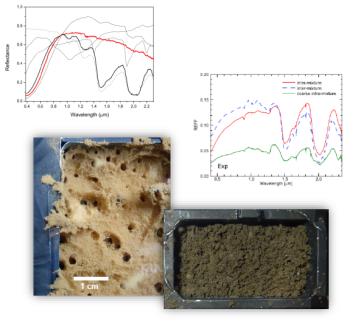
Near-IR reflectance spectra (0.4-2.4 µm) of water ice and smectite mixtures Poch et al., 2016b:
- evolution of the water/dust spectral features during sublimation
- water-free porous sublimation residues made of smectite
Near-IR reflectance spectra (0.4-2.4 µm) of biomolecules dry powders at 293±2 K Poch et al., 2017:
- proteins, DNA, phospholipids, carbohydrates, pigments
Near-IR reflectance spectra (0.7-4.0 µm) of spherical water ice particles:
- of well-controlled size distributions from about 2 to 100 µm
- produced with our Setups for the Production of Icy Planetary Analogues: SPIPA-A 4.5±2.5 µm, SPIPA-B 67±31 µm, SPIPA-C 2-100 µm
- at different temperatures (173 and 223 K)
- before/after metamorphism (sintering)
Data under ingestion in the BYPASS database
 Near-IR reflectance spectra (0.4-2.4 µm) of a pigmented microorganism (Deinococcus radiodurans) Poch et al., 2017:
Near-IR reflectance spectra (0.4-2.4 µm) of a pigmented microorganism (Deinococcus radiodurans) Poch et al., 2017:
- pure D. radiodurans hydrated or desiccated
- D. radiodurans mixed with silica sand (1010 organisms/mL) compared to pure silica sand
- D. radiodurans mixed with liquid water (1010 org./mL) compared to pure liquid water
- D. radiodurans inside water ice particles (105, 107, 109 org./mL) compared to pure water ice particles
- Evolution of D. radiodurans spectral signatures during sublimation of the ice
Near-IR reflectance spectra (0.4-2.4 µm) of water ice and dust mixtures:
Pommerol et al., 2015,Poch et al., 2016a,Poch et al., 2016b,Jost et al., 2017
- mixture of water ice and silicates (olivine, smectite)
- mixture of water ice and carbonaceous matter (tholins, charcoal, carbon black)
- inter- or intra- particles mixtures of water and dusts
- evolution of the water/dust spectral features during sublimation
- water-free porous sublimation residues made of mineral and/or organic dust
